"Significant Changes Make This Version a Must Have Program!"

Macromedia's Flash MX 2004 is the newest version of their web design program. Flash has come a long way since it was introduced by a small tech startup called FutureSplash. Macromedia bought the company and has established Flash as a standard for creating dynamic interactive web content. Thus, this simple web drawing and animation package has involved into a complete web application development environment. Its major technology innovations include sophisticated drawing and animation tools; a timeline for sequencing elements and controlling their behavior over time; the powerful ActionScript programming language for adding programmatic control and logic; support for rich media, such as MP3 audio and full-motion video; database connectivity capabilities; and re-usable components and templates for application development. With this introduction of Flash MX 2004, Macromedia has again enhanced the features and made significant changes.
One of the major differences is that there are now two different editions: Flash MX 2004 and Flash MX Professional 2004. Flash MX 2004 ships with the Studio MX 2004 bundle unless you opt to pay the additional fee for Professional. Flash MX Professional 2004 contains everything that Flash MX 2004 contains plus some added features such as project management tools, as well as external scripting capabilities to handle dynamic data from databases.
Further enhancements and changes have been made throughout the program from the new Timeline effects to a History panel to the use of ActionScript 2.
Flash MX 2004 is available for Macintosh and Windows with a price of $499 for the packed product and the electronic software download; Upgrade price is $199. Education edition price is $99. Macromedia has an excellent site to visit, with loads of information, freebies, & tutorials: http://www.macromedia.com.
![]()
New and enhanced features includes the following:
- Timeline Effects--You can now apply effects, including transitions such as fade-ins, spins, and more, to objects on the Stage.
- Behaviors--From the Behaviors panel, you can add interactivity without writing any code at all.
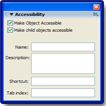
- Accessibility Support and Components --Now accessibility support is built in to make your Flash creations accessible. With the new accessibility features and components, there is now tab ordering, tab focus management, and support for screen readers and closed-caption programs.
- Updated Templates--Jump-start your projects with templates for common applications including learning interactions, interactive presentations, photo slide shows, and video presentations.
- Integrated Help System--The Help system is now integrated into the Flash environment, providing context-sensitive reference and tutorials.
- Spell Checker--You can now check your movies for spelling errors.
- Document Tabs--Document tabs displaying the name of each open document make it easy to switch between documents. This is a Windows-only feature.
- Start Page--The Start page provides quick links to recently used documents and to Macromedia for additional tutorials. You can also quickly open an existing file or open a new Flash file.
- Find and Replace--You can use the Find and Replace feature to locate and replace a text string, a font, a color, a symbol, a sound file, a video file, or an imported bitmap file.
- ActionScript 2--Flash MX 2004 now supports ActionScript 2, which follows the ECMA script language specification and supports inheritance, strong typing, and event model.
- History Panel--All your actions are tracked in the History panel and you can then use the history steps to create custom commands.
- Video Import Wizard--The Video Import Wizard has presets and clip editing to streamline your editing tasks.
- Small-font Size Rendering--You now have better support for crisp and clean-looking small fonts.
- Publishing--The new publishing features have options for better accessibility and Flash Player detection.
- Flash Player Detection--Your SWF files can now detect if the user has the required Flash Player version.
- Enhanced Globalization & Unicode Support--You can now author multilanguage text using any character set.
- Strings Panel--You can publish Flash content in multiple languages using the new Strings panel.
- Security--The Flash Player 7 offers stricter security than previous versions. When content is shared between two different domains, a pop up asks to allow or deny such access.
- Better Runtime Performance-- Flash Player 7 runtime performance is now two to five times better for video, scripting, and display rendering.
With Macromedia Flash MX 2004, it's easy to accelerate common timeline interactions and reduce the need for explicit key frame animation and manipulation. Common tasks that formerly required repetitive actions can now be achieved quickly with one step. Effects are non-destructive which means they can be repeatedly modified or removed after they have been applied. The effects include: Transition, Transform, Copy to Grid, Distribute Duplicate, Blur, Drop Shadow, Expand, and Explode. See image to the right for an example of the dialog box in Flash MX 2004 and the effects options.
From the Behaviors panel, you can add interactivity to Flash content without writing a line of code. For example, you can use behaviors to include functionality that links to a web site, loads sounds and graphics, controls playback of embedded videos, plays movie clips, and triggers data sources. This reduces the need to script simple tasks and automates your workflow.
You can create Flash content that is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, using the accessibility features provided with Macromedia Flash MX 2004. For example, you could design for the visually impaired users who might rely on assistive technology, such as screen readers that provide an audio version of screen content, and hearing-impaired users who might read text and captions in the document. Or you could design with other considerations in mind such as for users with mobility or cognitive impairments.
Flash MX 2004 includes updated templates for creating presentations, e-learning applications, advertisements, mobile device applications, and other commonly used types of Flash documents.
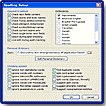
The Check Spelling feature enables you to check spelling in text throughout your Flash document. You can use Spelling Setup to select a variety of options for spell checking:
- Select document options to specify which elements in a Flash document are to be checked, including text fields, scene and layer names, frame labels and comments, and others.
- Select one or more built-in dictionaries to use when checking spelling.
- Create a personal dictionary with words and phrases you add yourself.
- Select checking options to specify ways to handle specific word and character types, such as nonalphabetic words or Internet addresses, when spell checking.
When you open multiple documents in Windows, tabs at the top of the Document window identify the open documents and let you easily navigate among them. Tabs appear only when documents are maximized in the Document window. To make a document active, you click its tab. By default, tabs appear in the order in which the documents were created. You cannot drag tabs to change their order.
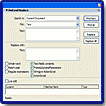
You can use the Find and Replace feature to find and replace a specified element in a Flash document. You can search for a text string, a font, a color, a symbol, a sound file, a video file, or an imported bitmap file.
You can replace the specified element with another element of the same type. Depending on the type of specified element, there are different options available in the Find and Replace dialog box.
You can find and replace elements in the current document or the current scene. You can search for the next occurrence or all occurrences of an element, and you can replace the current occurrence or all occurrences.
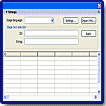
The History panel shows a list of the steps you have performed in the active document since you created or opened that document, up to a specified maximum number of steps. (The History panel doesn't show steps you’have performed in other documents.) The slider in the History panel initially points to the last step that you performed.
You can use the History panel to undo or redo individual steps or multiple steps at once. You can apply steps from the History panel to the same object or to a different object in the document. However, you cannot rearrange the order of steps in the History panel. The History panel is a record of steps in the order in which they were performed.
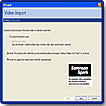
The Video Import wizard provides a streamlined interface for importing video into a Flash document. The wizard lets you select whether to import a video clip as an embedded or a linked file.
When you import a video clip as an embedded file, you select options in the wizard for encoding and editing the video. Click the Next button to advance through panes in the wizard, and click the Back button to return to previous panes.
You can import video clips as embedded files in several file formats, depending on your system. You can preview frames of an imported video by dragging the playhead along the Timeline. However, the sound does not play back.
The Alias Text button in the Property inspector lets you render text so that it appears more readable at small sizes. This option is supported for static, dynamic, and input text if the end user has Flash Player 7 or later. It is supported only for static text if the user has an earlier version of Flash Player.
The Alias Text option makes small text more readable by aligning text outlines along pixel boundaries. This makes the text appear aliased, even when anti-aliasing is enabled. When Alias Text is enabled, all text in the current selection is affected. The feature operates with text of all point sizes in the same way.
You can now publish SWF files with associated files that detect if a user has a specified Flash Player version. You can configure your published files to direct users to alternate files if they don't have the specified Flash Player.
As more applications are distributed to worldwide audiences, it is becoming common to author applications that can appear in multiple languages. Macromedia Flash MX 2004 provide several new features that greatly enhance the work flow for authoring multiple language Unicode-based applications.
The new Strings panel in Flash MX 2004 lets localizers edit strings in a central location inside Flash or in external XML files with their preferred software or translation memory. A string is a sequence of characters such as letters, numbers, and punctuation marks. There are several ways to assign text strings to the Strings panel. This makes the string panel very useful. You can assign a string ID to a dynamic or input text field, add a string to the Strings panel without assigning it to a text field, or assign an existing string ID to an existing dynamic or input text field.
PC:
- 600 MHz Intel Pentium processor or equivalent
- Windows 98, Windows 2000, or Windows XP
- 128 MB RAM (256 MB recommended by Macromedia)
- 347 MB available disk space (More if you plan on storing your Flash files on the hard drive)
Mac:
- 500 MHz Power PC G3 processor
- Mac OS X 10.2.6 and later, 10.3.4
- 128 MB computer RAM (256 MB recommended by Macromedia)
- 280 MB available disk space (More if you plan on storing your Flash files on the hard drive)
Web Page Design: Macromedia Dreamweaver MX 2004
| Educational | Books | Utilities | Web Tools | Legal | Articles